
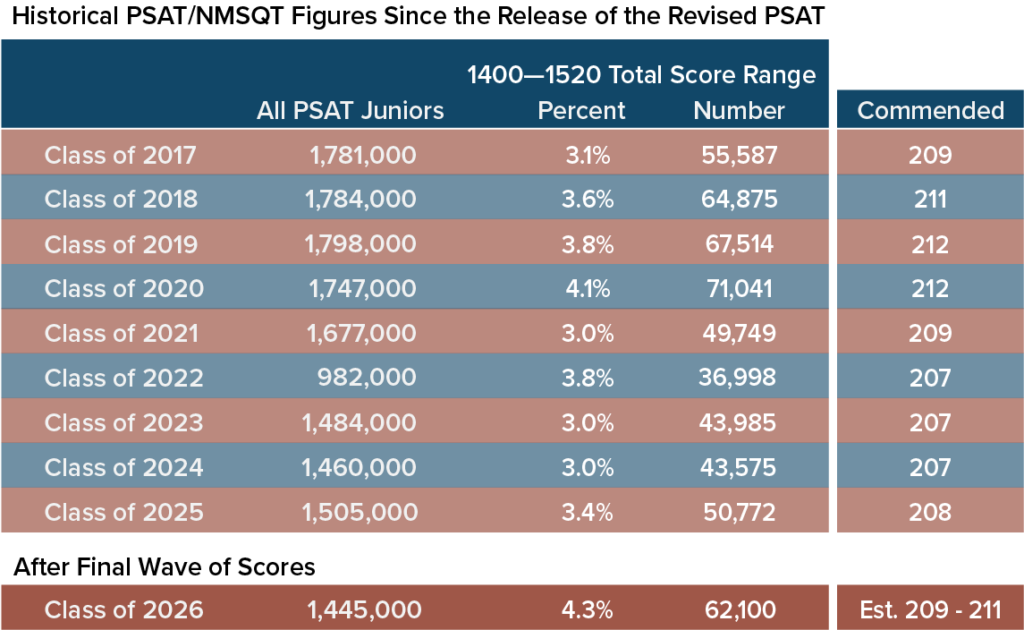
Record High National Merit Scores Announced
Every year, the National Merit Scholarship Program honors approximately 17,000 students as National Merit Semifinalists based on junior year PSAT scores. Semifinalists can continue in the competition to become Finalists and, potentially, scholarship recipients. Current Semifinalists and future participants may want to read Compass’s National Merit Scholarship Program Explained for more information on the steps in the program. An additional 40,000 students are honored as Commended Students for having scores in the top 3% of all test takers. The recently confirmed cutoffs reveal that the Class of 2026 had the highest Semifinalist scores ever on the PSAT. Of the 12 largest states, 8 set new records and the other 4 tied their highest historical marks. Students in Massachusetts and New Jersey (225) would have needed to score at least a near-perfect 750 on the Reading & Writing (RW) and combine it with a 750 or 760 on Math.
The large jump points to a problem
The nearly universal increase in Selection Index cutoffs is most likely attributable to a flaw in scaling or test construction that produced higher scores on both Reading & Writing and Math. Since these sorts of scoring changes can also occur on the SAT, this post explores the implications for National Merit and college admission testing.
Scaling error best explains:
- Why there were changes across the entire score range
- Why there was a change in almost all states
- Why new records were reached in so many states, particularly the largest states
It’s the sort of shift we have seen before, but there are some added twists this time.
How cutoffs are determined
Qualifying scores (“cutoffs”) are not based on the total score for the PSAT (360-1520) but on the Selection Index, which is calculated by doubling the RW score, adding the Math score, and then dividing the sum by 10. The maximum Selection Index is 228. Students can find a historical set of cutoff data here or see how Semifinalist and Commended counts have changed state by state.
Semifinalists are allocated by state, and cutoffs are calculated by state. This means that students across the country face varying qualifying scores for Semifinalist status (the Commended level is set nationally). The cutoffs for the Class of 2026 range from 210 in New Mexico, North Dakota, West Virginia, and Wyoming to 225 in New Jersey and Massachusetts. If California is allocated 2,000 Semifinalists based on its population of high school graduates, then NMSC works down from a perfect 228 Selection Index until it gets as close as possible to that target. This year, California’s 224 included 2,172 students. A cutoff of 225 would have produced too few Semifinalists. A cutoff of 223 would have gone well over the allocation.
Below are this year’s cutoffs compared to those from prior years. The Class of 2026 figures are confirmed.
| State | Class of 2026 (Actual) | Change | Class of 2025 (Actual) | Class of 2024 (Actual) | Semifinalists | Commended |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 214 | 2 | 212 | 210 | 228 | 141 |
| Alaska | 215 | 1 | 214 | 209 | 31 | 24 |
| Arizona | 218 | 1 | 217 | 216 | 409 | 557 |
| Arkansas | 215 | 2 | 213 | 210 | 141 | 106 |
| California | 224 | 3 | 221 | 221 | 2172 | 6840 |
| Colorado | 219 | 1 | 218 | 216 | 287 | 579 |
| Connecticut | 223 | 2 | 221 | 221 | 193 | 709 |
| Delaware | 220 | 1 | 219 | 219 | 47 | 84 |
| Florida | 219 | 2 | 217 | 216 | 1008 | 1824 |
| Georgia | 220 | 2 | 218 | 217 | 620 | 1243 |
| Hawaii | 219 | 2 | 217 | 217 | 60 | 124 |
| Idaho | 215 | 2 | 213 | 211 | 90 | 76 |
| Illinois | 222 | 2 | 220 | 219 | 748 | 1888 |
| Indiana | 218 | 1 | 217 | 216 | 333 | 531 |
| Iowa | 214 | 2 | 212 | 210 | 138 | 77 |
| Kansas | 216 | 1 | 215 | 214 | 136 | 113 |
| Kentucky | 214 | 1 | 213 | 211 | 200 | 121 |
| Louisiana | 216 | 2 | 214 | 214 | 220 | 219 |
| Maine | 217 | 3 | 214 | 213 | 57 | 63 |
| Maryland | 224 | 2 | 222 | 221 | 348 | 1290 |
| Massachusetts | 225 | 2 | 223 | 222 | 282 | 1754 |
| Michigan | 220 | 2 | 218 | 217 | 470 | 965 |
| Minnesota | 219 | 2 | 217 | 216 | 266 | 438 |
| Mississippi | 213 | 1 | 212 | 209 | 153 | 53 |
| Missouri | 217 | 2 | 215 | 214 | 281 | 326 |
| Montana | 213 | 4 | 209 | 209 | 48 | 8 |
| Nebraska | 214 | 3 | 211 | 210 | 109 | 63 |
| Nevada | 214 | 0 | 214 | 211 | 185 | 78 |
| New Hampshire | 219 | 2 | 217 | 215 | 51 | 99 |
| New Jersey | 225 | 2 | 223 | 223 | 511 | 3199 |
| New Mexico | 210 | -1 | 211 | 207 | 111 | 0 |
| New York | 223 | 3 | 220 | 220 | 992 | 3378 |
| North Carolina | 220 | 2 | 218 | 217 | 523 | 1151 |
| North Dakota | 210 | 0 | 210 | 207 | 26 | 0 |
| Ohio | 219 | 2 | 217 | 216 | 490 | 999 |
| Oklahoma | 212 | 1 | 211 | 208 | 214 | 39 |
| Oregon | 219 | 3 | 216 | 216 | 188 | 318 |
| Pennsylvania | 221 | 2 | 219 | 219 | 612 | 1511 |
| Rhode Island | 219 | 2 | 217 | 215 | 50 | 96 |
| South Carolina | 215 | 1 | 214 | 209 | 225 | 197 |
| South Dakota | 211 | 3 | 208 | 209 | 46 | 6 |
| Tennessee | 219 | 2 | 217 | 217 | 306 | 521 |
| Texas | 222 | 3 | 219 | 219 | 1673 | 4653 |
| Utah | 213 | 2 | 211 | 209 | 199 | 68 |
| Vermont | 216 | 1 | 215 | 212 | 27 | 27 |
| Virginia | 224 | 2 | 222 | 219 | 489 | 1912 |
| Washington | 224 | 2 | 222 | 220 | 388 | 1295 |
| West Virginia | 210 | 1 | 209 | 207 | 66 | 0 |
| Wisconsin | 215 | 1 | 214 | 213 | 287 | 216 |
| Wyoming | 210 | 1 | 209 | 207 | 20 | 0 |
| District of Columbia | 225 | 2 | 223 | 223 | 37 | 230 |
| Boarding Schools | 220-225 | 158 | 652 | |||
| U.S. Territories | 210 | 2 | 208 | 207 | 43 | 0 |
| Studying Abroad | 225 | 2 | 223 | 223 | 86 | 565 |
| Commended | 210 | 2 | 208 | 207 |
What the PSAT tells us about the SAT
Analyzing the PSAT/NMSQT is about more than just explaining National Merit cutoffs. The PSAT also provides a unique window into the SAT program. National Merit results offer comparable year-over-year data that are more granular than what College Board provides for the SAT. The scoring anomalies we saw on the October 2024 PSAT are also likely occurring on the SAT; they’re just better disguised on the three-letter exam. Based on our historical review, scoring outliers crop up every 3 to 4 years with the PSAT. Projected across an SAT cycle, that’s potentially 2 problematic exam dates every year!
Cutoff changes
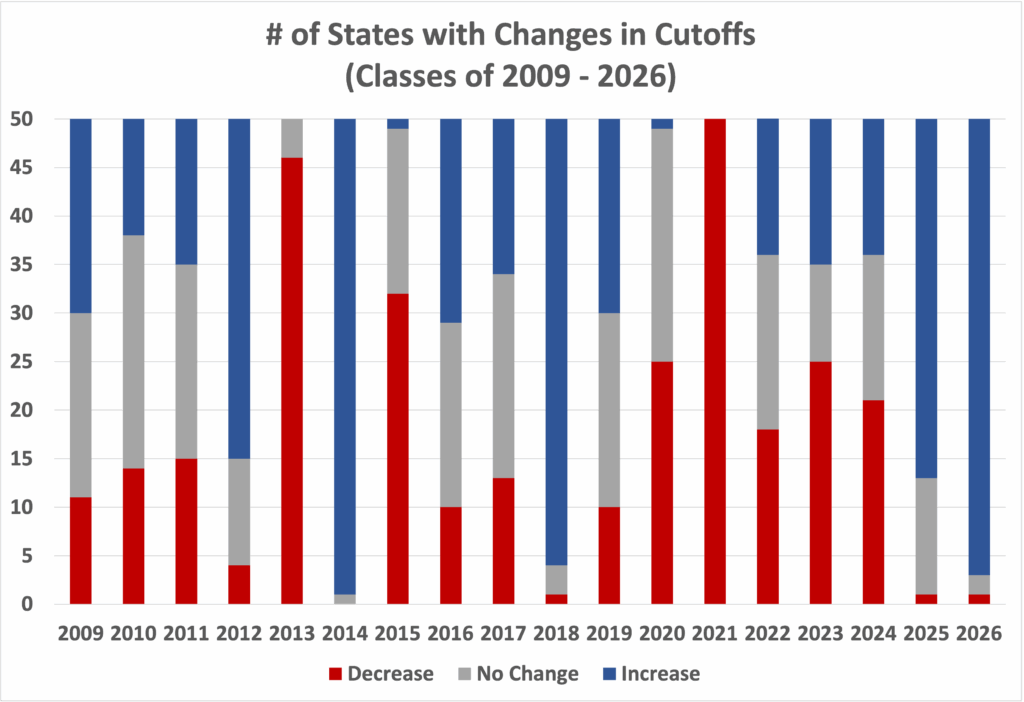
In total, 47 states saw higher cutoffs, as did the District of Columbia (225, a new record), U.S. territories and commonwealths (210), U.S. boarding schools (220-225, new records), and U.S. students abroad (225, a new record). Boarding school cutoffs are set at the highest state cutoff within the National Merit region. For students at day schools, eligibility is defined by the school’s location rather than the student’s home address.
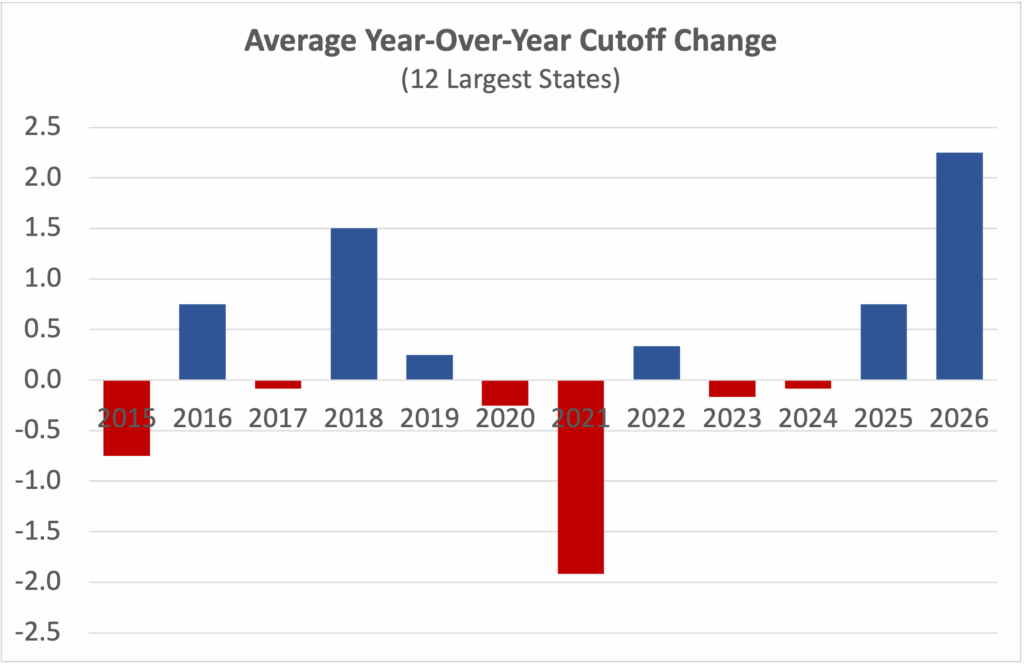
State cutoffs always have some degree of fluctuation, especially in smaller states. The size and consistency of this year’s movements set them apart, and large states provide the best measuring stick. A 3-point increase in Maine’s cutoff might be considered unusual, but a 3-point rise in California’s cutoff demands an explanation.
The 12 largest states account for more than 10,000 Semifinalists. Their cutoffs went up an average of 2.25 points, a record change. Even the plunge in the Class of 2021, traced back to a flawed PSAT form, was more moderate.
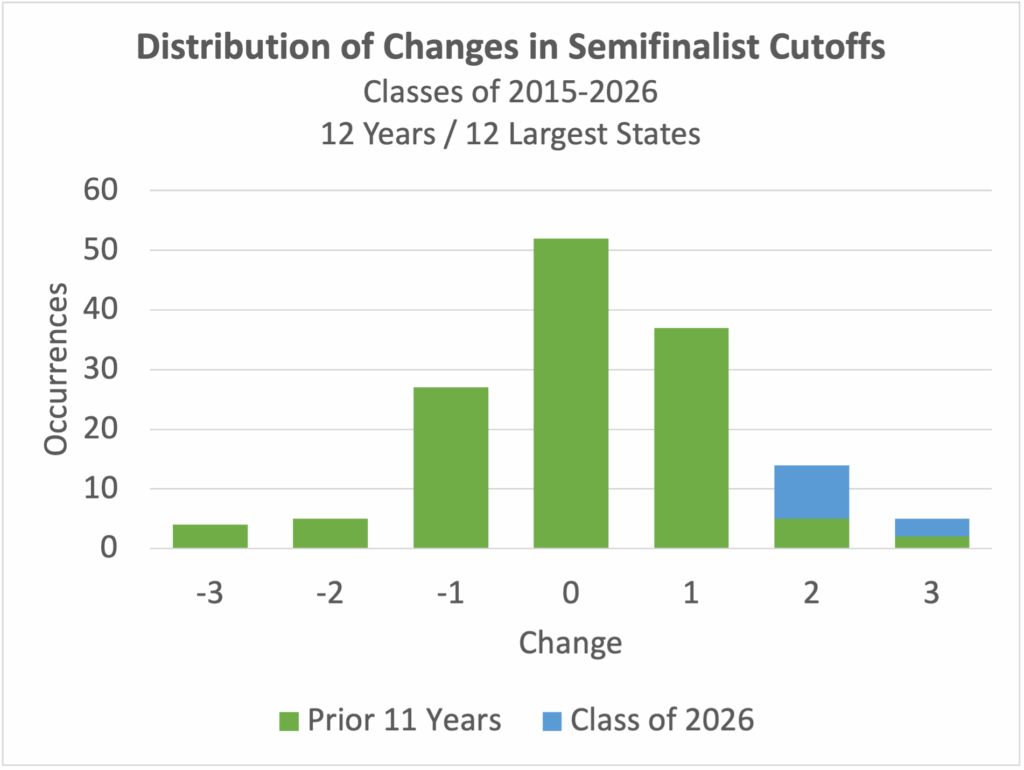
Over the last dozen years, the majority of 2- and 3-point changes in large states’ cutoffs occurred just this year.
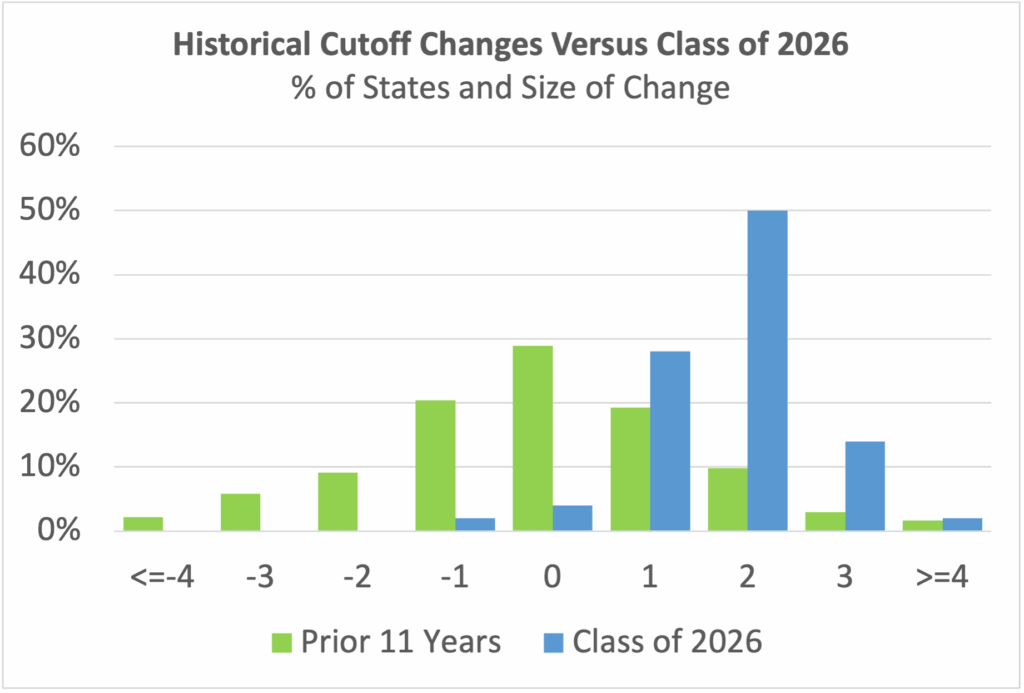
The bias is also seen when looking at all 50 states. The chart below shows how changes in the prior 11 years compare to the Class of 2026’s shifts. Historically, cutoffs remain unchanged approximately 30% of the time, and go up by 2 or more points only 15% of the time. This year, two-thirds of states saw increases of 2 or more points.
Was the PSAT fair? Was it wind-assisted?
In running events such as the 100m-dash, results do not qualify as world records if there is too much wind. The race results still stand; the gold, silver, and bronze medalists still finished first, second, and third. But the runners’ performances are not comparable to other races if they had a 15-mile per hour wind at their backs. While the October 2024 PSAT was likely wind-assisted, it was largely fair to those taking the test. The higher National Merit cutoffs did not alter the number of Commended Students or Semifinalists. Students were still ranked 1, 2, 3, etc.
Why the qualifier of “largely fair”?
On the digital PSAT, not all students answer the same questions. There is a pool of potential items. Nor is scaling done by a simple tally of right/wrong answers. As with the digital SAT, a specialized form of scoring called 3-parameter Item Response Theory (IRT) is used on the PSAT. IRT is a form of pattern scoring, where a student’s score is determined by which specific questions are answered correctly or incorrectly. If the parameters for questions were inaccurate and those questions only went to certain students, then the bias in scores may not have been uniform. A swirling wind could have helped some students and not others. The consistency of the upward bias, though, indicates that most students were boosted last October.
Scores provide needed insight
In the old world of paper PSATs, College Board shared select test forms with students, provided educators with performance data for questions, and released scales. None of that takes place with the digital PSAT. No items are released. No scoring parameters are provided. No performance data is shared. Students are not even told how many questions they got right or wrong. In short, visibility over the exam is available only by analyzing reported scores.
Those reported scores clearly show the upward bias. The number of students earning a 700-760 score on Reading & Writing increased from 62,000 to well over 74,000 (a 20% increase). The number of Math scores in that range went from 59,000 to approximately 78,000 (up more than 30%).
The changes at the very top were likely even more extreme. With the 223 cutoff seen in New Jersey for the Class of 2025, there were 12 score combinations that qualified a student for Semifinalist: 740RW / 750M, 740RW / 760M, etc. For the state’s 225 cutoff this year, there were only 6 combinations. It’s possible that the number of 750-760 scores went up by 50% or more.
So, the October 2024 test was easier than normal?
If easier is defined as more students able to achieve top marks, then the answer is “yes.” That doesn’t mean that the questions themselves were easier. The test’s scale is meant to adjust for differences. Somewhere along the line, things broke down.
Over the last two decades, the PSATs from 2011 (Class of 2013), 2016 (Class of 2018), 2019 (Class of 2021), and 2024 (Class of 2026) stand out as problematic. In those years, almost every state saw a change in cutoffs, and the direction and size of the change point to non-parallel forms (wind!). (The Class of 2014 also saw significant changes, but those were more of a bounce-back from the previous year.) The anomalous 2019 results could be traced back to a particularly mis-scaled form, which I wrote about at the time.
Implications for the SAT
The PSAT offers a snapshot of an entire class at a specific moment. In contrast, the SAT is administered on various dates and times, yet all results are reported as interchangeable. Some SAT takers may have wind at their backs, and some may be running directly into the wind. College Board’s goal is to prevent differing conditions or factor them out of the equation. Its objective is to ensure that the questions on each exam are nearly identical in content and difficulty (known as “parallel forms”), with any minor discrepancies accounted for through equating and scaling. However, PSAT results highlight the challenge of achieving this goal. Ultimately, some SAT administrations are going to yield higher or lower scores, just as observed with the PSAT.
Why aren’t you analyzing those SAT changes?
SAT data provided by College Board tend to obscure non-parallel results. Scores from individual test dates are not publicly shared. Even in the locked-down educator portals, scores are only reported in broad ranges. By the time College Board presents the results for a group of graduated students, the impact of non-parallel forms has been smoothed away, and College Board prefers it that way. If you can’t see scoring irregularities, did they really happen? The useful thing about the PSAT is that we can see them. National Merit cutoffs are far more granular than the 1400-1600 range that College Board reports annually for the SAT.
Non-parallel forms, norms, and student behavior
If test forms are not consistently parallel, then students have added incentive to repeat the SAT. As a test taker, why wouldn’t I want to stumble across an exam with an upward bias? The incentive is increased by the fact that superscoring locks in any upward bias and any positive error (see below) on each section of the test. Over time, the number of test dates taken by students applying to competitive colleges has increased, and testing calendars have shifted forward to allow for this. This may not be desired behavior, but it is rational behavior.
Due to upward shifts in SAT scores, traditional normative data like percentiles are insufficient for accurately measuring performance. PSAT students in the class of 2026 saw how tricky it can be comparing one’s performance to historical norms. The same problem arises on the SAT. Percentiles are provided for the three preceding class years. If there is an upward shift, it will not be fully reflected for more than three years. Unlike the ACT, College Board stopped reporting the number of students achieving each score nearly a decade ago and has never disclosed the impact of superscoring on score distribution. When assessing where an SAT score really ranks, students are not given the full picture.
In effect, College Board provides outdated track season averages for the SAT and expects them to be good enough to assess individual race results. Wind be darned.
Haven’t scores always been volatile?
Fluctuations at the individual level are different than those at the population level, although both can contribute to scoring uncertainty for students.
All tests contain inherent imprecision, known as the standard error of measurement (SEM) in psychometrics. SEM reflects that a single test can not accurately pin down a student’s “true score.” For this reason, College Board provides students with a score range, typically plus or minus 30 points, beneath their reported test scores.
Changes in the National Merit cutoffs can not be explained by SEM. Error in measurement is effectively random, and negative error and positive error cancel out when viewed over a large population. It doesn’t get much larger than the 1.5 million juniors who took the PSAT. SEM would not push scores upward.
The confidence intervals provided on student scores, however, assume parallel forms. Non-parallel forms are the likely cause of the increases on the October 2024 PSAT.
Instead of random error, scores were biased upwards, at least at the highest levels. There is strong circumstantial evidence that the October 2024 PSAT was not parallel to the October 2023 PSAT. In other words, students saw volatility (College Board’s inability to equate each test to produce equivalent scores) layered on top of typical volatility (the fluctuation of individual student scores due to SEM). The same problem arises with the SAT, it is simply hidden from view.
Fluke, shift, or trend
Was the observed bias on the PSAT a fluke, shift, or trend? The change in score distribution could be attributable to something unique to the October 2024 PSAT. We saw this happen with the paper tests in the past. There were outlier years that we might consider “flukes.”
Alternatively, we could be seeing a permanent shift upward in scores. Instead of wind at the back, are we perhaps seeing a move to a new track surface that will permanently raise scores? Equating a new test format is difficult. Equating a new format that accounts for future student behavior is even harder. Is it simply coincidence that scores jumped in both 2016 and 2024, the years after the introduction of new PSAT designs? It’s difficult to disprove a shift at its very outset.
Could the change reflect even more than a shift? Could it be a trend that will push scores higher still? This seems like the least likely possibility. Previous examples of major score differences have fallen into the fluke or shift buckets.
Other theories about the change
There are other theories as to why PSAT scores increased. For example, is the increase in PSAT scores due to better preparation? It is unlikely. I have spent much of my professional life helping students improve their test scores, so it may seem odd that I discount learning improvements or test preparation as an explanation. Practice and preparation do raise scores at the individual level. The behavior of a testing population, however, rarely changes quickly or uniformly.
The cutoffs in the largest 12 states went up either 2 points or 3 points. We should not have seen that uniformity if preparation and technique were the primary causes.
It’s Desmos’ fault
Probably not. Desmos, the powerful online calculator available for the PSAT and SAT, was available in 2023, as well. Students may have become more adept with Desmos, but that doesn’t explain why we also saw an increase in Reading & Writing scores. Further, a Desmos-linked impact should be less prominent at the highest score levels, since students capable of scoring 740-760 are less likely to see the benefit versus those scoring, say, 650-700.
Are the cutoffs explainable by a change in testing population?
The number of students taking the PSAT can change from year-to-year. The score level of those students can also change. For example, if a state begins requiring all students to take the PSAT, the average score will go down, while the number of high scorers may move up (in previous years, we saw this in Illinois and Michigan). This is a poor fit for what we saw with the PSAT. Scores went up across virtually all states. There is strong evidence that there were forces that pushed Selection Indexes up by 2 points.
Is the change attributable to the adaptive nature of the exam?
The RW and Math PSAT each have two stages. A student receives an initial set of questions. Based on their performance on that first stage, the student receives a set of easier or harder problems in stage 2. An adaptive test can more quickly narrow down a student’s score, but there is always the chance of what is known as routing error. In other words, a student with an ultimate score of 640 probably should have been routed to the harder stage 2 problems rather than the easier ones. There may be less accuracy had the student been routed to the easier set of questions. However, routing error should be neutral for the population as a whole. Further, College Board research maintains that routing error has a minimal impact on scores. Most important, students scoring at the National Merit range would have been routed to the harder stage 2 with 99+% certainty.
IRT scoring may have been a factor. Item parameters are calculated beforehand through pre-testing, where the question is included as an unscored item on earlier exams. Inaccurate parameters can lead to inaccurate scores.
The digital PSAT and SAT are shorter than their paper ancestors, and this can contribute to score instability. An individual problem or two plays a greater role on a shorter exam. While this can be offset by the adaptive nature of the test, longer is always better when it comes to test reliability. The PSAT tries to place students on a 160 to 760 scale with only 40 scored Math questions and only 50 RW questions.
Could NMSC have changed how it calculates cutoffs?
Each year, some students are unable to take the PSAT because of illness or other extenuating circumstances. These students can apply to enter the scholarship program via Alternate Entry using an SAT score. The deadline for application is generally April 1 after the PSAT, although students can use SAT scores through the June test date. In the past, NMSC has only used PSAT scores to calculate cutoffs (with an exception made during the COVID-related cancellations in 2020). Because students can take the SAT on multiple dates, their scores skew higher than PSAT scores. If NMSC were to include them in the cutoff calculations, it would likely lead to cutoff inflation. Compass has not heard that any changes were made for the Class of 2026.
Did Compass see the changes coming?
Only in part. Once PSAT scores were available in November, we noted the uptick in 1400-1520 scores and projected that the Commended cutoff would move up 2 points to 210. While upward movement was expected nationally, we did not foresee the breadth of the changes. The table below shows that there were far more high scores in the Class of 2020. The class also saw a higher Commended of 212. Yet the highest Semifinalist cutoff only reached 223. Cutoffs as high as 225 were without any precedent.
What about expectations for the Class of 2027 and beyond?
More than ever, PSAT students have to be aware that “past performance is no guarantee of future results.” In November, Compass will report on the scoring of the October 2025 exam and provide our range projections. We won’t know what future cutoffs will be, but the PSAT scores may provide clues on the question of fluke, shift, or trend.
Why does each state have its own Semifinalist cutoff if the program is NATIONAL Merit?
This is always a hot button question. NMSC allocates the approximately 17,000 Semifinalists among states based on the number of high school graduates. That way, students across the nation are represented. It also means that there are very different qualifying standards from state to state. A Massachusetts student with a 220 might miss out on being a Semifinalist. If she lived 10 miles away in New Hampshire, she would qualify.
NMSC sets a target number of Semifinalists for a state. For example, California sees about 2,000 Semifinalists every year, Michigan 500, and Wyoming 25. In each state, NMSC determines the Selection Index that comes closest to matching its target number of Semifinalists. If 1,900 California students score 222 and higher and 2,050 score 221 or higher, then the Semifinalist cutoff would be 221 (this assumes that the target is exactly 2,000). Because score levels can get crowded, it is easy for cutoffs to move up or down a point even when there is minimal change in testing behavior or performance.
No Semifinalist cutoff can be lower than the national Commended level. Cutoffs for the District of Columbia and for U.S. students studying abroad are set at the highest state cutoff (typically New Jersey). The cutoff for students in U.S. territories and possessions falls at the Commended level each year. Boarding schools are grouped by region. The cutoff for a given region is the highest state cutoff within the region.
When are National Merit Semifinalists announced for the next class?
The Commended cutoff will become unofficially known by the end of April 2026. The lists of Semifinalists will not be distributed to high schools until the end of August 2026. With the exception of homeschoolers, students do not receive direct notification. NMSC asks that schools not share the results publicly until the end of the press embargo in mid-September, but schools are allowed to notify students privately before that date. NMSC does not send Commended Student letters to high schools until mid-September. Compass will keep students updated on developments as the dates approach.
Do state and national percentiles indicate whether a student will be a National Merit Semifinalist?
No! Approximately 1% of test takers qualify as Semifinalists each year, so it is tempting to view a 99th percentile score as indicating a high enough score — especially now that College Board provides students with percentiles by state. There are any number of flaws that rule out using percentiles as a quick way of determining National Merit status.
- Percentiles are based on section scores or total score, not Selection Index
- Percentiles are rounded. There is a large difference, from a National Merit perspective, between the top 0.51% and the top 1.49%
- Percentiles reveal the percentage of students at or below a certain score, but the “at” part is important when NMSC is determining cutoffs.
- The number of Semifinalists is based on the number of high school graduates in a state, not the number of PSAT takers. Percentiles are based on PSAT takers. States have widely varying participation rates.
- Most definitive of all: Percentiles do not reflect the current year’s scores! They are based on the prior 3 years’ performance. They are set even before the test is given. And if you are going to use prior history, why not use the record of prior National Merit cutoffs rather than the highly suspect percentiles?
Entry requirements for National Merit versus qualifying for National Merit.
Your PSAT/NMSQT score report tells you whether you meet the eligibility requirements for the NMSP. In general, juniors taking the October PSAT are eligible. If you have an asterisk next to your Selection Index, it means that your answers to the entrance questions have made you ineligible. Your answers are conveniently noted on your score report. If you think there is an error, you will also find instructions on how to contact NMSC. Meeting the eligibility requirements simply means that your score will be considered. Approximately 1.4 million students enter the competition each year. Only about 55,000 students will be named as Commended Students, Semifinalists, Finalists, or Scholars. See National Merit Explained for more information.


Hi Art,
I have a 217 in Michigan. Any updates on the cutoff?
Thank you!
Not yet, but I expect a large set of updates Tuesday morning.
So if I have a score of 218 in Texas is there no chance of becoming a semifinalist?
I’m sorry, Louisa, but that is correct.
Hello Art,
Will IL cutoff be at 219 or 218?
Thanks,
GA
Illinois is confirmed at 219!
Hi Art, how did we find out the score cutoff for Georgia? I’m just curious because I have a 219 and am a little nervous. Thanks!
Georgia’s official cutoff is 218. I just posted the complete list.
Any word on Delaware 219?
Delaware’s cutoff was 218 this year. Congratulations!
Hi, Art. I scored a 216 in Ohio. You said in another comment that a 217 should qualify, so do you have any new information?
A 216 qualified. Congratulations! We just posted the full list of cutoffs.
215 Ohio not qualified?
Adrees,
That’s correct. 216 or higher qualified in Ohio.
Not helpful at all since we already know the highest cutoff is a 223, but a 224 qualified in Colorado…
Congratulations, A! We just posted all of the official cutoffs.
Hi Art,
I just wanted to say thank you again for all of your work on this. It really helped alleviate a lot stress knowing the cut-off early. It was also great theater watching the scores roll in!
Hello, Art. I got a 220 in Massachusetts. Is this sure to qualify for NMSF?
Thank you!
Alex,
As long as you are not a boarding school student, it will qualify.
Does a 215 in AZ qualify for national merit semifinalist?
Yes, the cutoff is 214.
Do you happen to know – Were the high schools notified of their school’s semi-finalists today?
Notifications were mailed to schools about 2 weeks ago, which is why information has been filtering in. There is no single procedure for schools to notify students, but many will wait until next week when the press embargo ends.
Thanks! Your articles have been super helpful!!!!
I qualified as a semifinalist (yay!) and also have a confirming sat score. Is there anything else I can really do now to improve my application before October? Thanks for the cutoff information, you saved my friends and I a good deal of stress!
Mavo,
Congratulations! And I’m glad I could help. You can start on your Finalist essay and stay out of trouble at school! That’s about all you need to worry about at the moment.
I called high school principal this afternoon to see if my son made the NMSF, he said that he didn’t get anything from college board or NMSC yet! Is it possible?
Yes, it’s possible. I recommend patience in these situations. NMSC won’t be helpful until after the press embargo ends next week, but my experience is that they will be very helpful after that date. And the mail will have likely shown up by that point.
I’m a student in Texas and my school notified me that I made it as a semifinalist.
Congratulations, Steven!
Hi Art
Thank you for your time and service. From MA 222 but have not received any information from school. It is a catholic school. would that matter?
MaryAnn,
No, it shouldn’t matter. Many schools will wait until the press embargo ends next week. I would give it until next Wednesday and then contact your counselor. As a distraction, you can start thinking about the Finalist essay. Unless they have changed it this year: “To help the reviewers get to know you, describe an experience you have had, a person who has influenced you, or an obstacle you have overcome. Explain why this is meaningful to you. Use your own words and limit your response to the space provided.”
Hi Art,
Can you explain the “press embargo”? Does the letter to schools specifically instruct them not to tell anyone until next Wednesday? And, if so, why are we hearing so many reports? According to your numbers, my son should be a finalist (222 in IL), but I’m getting a little anxious.
I don’t have the exact wording, but my recollection is that it asks schools not to “make the information public” until the announcement date. Many schools read this as only restricting public release — so avoiding things like school assembly announcements or a piece in the school newspaper. Some schools read the language as meaning that it should keep the list of students secret until the announcement date. I would feel a bit more sympathetic to NMSC’s desire for secrecy if the press release date actually saw all students being notified. Instead, NMSC only notifies schools and the press, so many students are left hanging. It’s well past time for NMSC to institute electronic notification. It’s worked for virtually every college in the country; it can work for the National Merit Scholarship Program.
Hi. Can you elaborate on “limit your response to the space provided”? Does that translate to a character or word count? Are you able to repurpose a Common App essay if it fits the prompt without editing it or is the “space provided shorter than 650 words? Thanks.
It is a combination character/space limit. Your Common App essay can likely be repurposed. Last year’s language: “We estimate your essay should be about 3,500 characters; however, you must preview your work to make sure that your essay fits in the space provided on the PDF. Any text that does not appear on the PDF will not be read or considered, even if it is within the character limit.”
Hi Art,
Thank you for all you do!! I am wondering about our Finalist application- how good do our essays, activities, etc need to be to get this status (if you have any idea)? Just worried about this along with college apps..
AFAIK, the essay and activities are not a part of qualifying as a Finalist. Those are used at the scholarship phase. The good news is that the application is not daunting. The essay prompt is general enough that you’re likely already writing something that works. The rest of the application takes about 15 minutes (assuming you’ve already gathered much of the basic info for your college apps). If you’ve got a confirming SAT/ACT score, then you’re set on that score. Grades matter, but that’s out of your control at this point.
HI. Thanks for all the great details. On the grades, which quarter or semester do they look through — end of junior year, Edna of senior Q1 or end of senior senior semester 1?
Given the timing, I think it could only be through junior year for Finalists. I can’t swear that NMSC doesn’t ask for an update from schools when considering scholarships.
About the first-choice college, do we put any college or have to pick one from the sponsor colleges? When would be the last date to change the college? Thanks!
The scholarship matching process begins March 1. You can change your choice after that date, but you risk being mismatched and losing the opportunity for a scholarship.
You don’t HAVE to choose from among sponsoring colleges, but that means you will only be available for NM and corporate-sponsored awards.
I’m confused about the “Confirming SAT Score”. Does that mean the semi-finalist’s SAT score should also be above the state cut-off for Semi-finalist cutoff? I also thought I read somewhere it only needed to be above the Commended Scholar cutoff? Thanks for your excellent updates, Art and Compass Group. You have been the best source of information about many test-related questions for many years!
The confirming score is set nationally; no, a student does not need to reach the state’s Semifinalist cutoff. NMSC doesn’t come right out and say that the confirming cutoff and the Commended cutoff are the same, but it is true or approximately true. Thank you!
Hello Art,
Is it possible CA cutoff is 221 but not 220?
Thank you.
The CA cutoff is 220. Period.
Nevada has the biggest drop since 2020–from 218 to 210. First, is 210 absolutely confirmed? Second, would it be attributed to low participation or “learning gaps”?
Absolutely confirmed. Small states can see large swings from relatively minor changes, especially when their cutoffs are on the low side because scores tend to be clumped together. Nevada saw 162 NMSFs this year as opposed to 114 last year and 112 the year before. That means the cutoff was probably not that far from being 209! It’s hard to know which of the factors played a role. The number of Semifinalists + Commended Students has remained fairly constant the last 3 years at 220-230. So for some reason there were as many students reaching Commended, but many more getting stuck at just a few points above Commended. I’d say scoring anomalies, learning gaps, and participation rate all could have played a role. Also, all it takes is a few powerhouse schools to drop out to shift things in Nevada. Bottom line: I don’t know.
Thanks for the reply! 162 is a big jump from 114. Does that mean NMSC was targeting Semifinalist count ~114, but there were too few >=211 and a whole lot of 210s?
Or that they are targeting around 130, perhaps, and that some years giver more or less because of how the distribution plays out. It means a lot of 210s. It’s harder to say about 211s because by the time they hit 162, they weren’t even going to take the 163rd.
Art
Since there are only 16000 NMSF each year, if Nevada had 162 with target 130, does that mean the increase was adjusted with other state targets? Did New Jersey meet its target number for NMSF or fewer to adjust variance with other states?
It usually works out to closer to 16,500 or so. I’m not entirely sure, but keep in mind that some schools are going to be a bit above target and some will be a bit below. So it’s not as simple as “this school got more so we need to take them away from other states.” New Jersey was on the low side, presumably because it had a large number of students at 222.
I made the TX cutoff with a 220 and have a confirming SAT score of 221 … any idea what GPA is required to make it to finalist?
No, NMSC does not release a GPA cutoff.
Hi Art,
Do you know how many NMSF’s California had this year?
I don’t know the exact number, but it is generally a bit over 2,000.
Question about the term “cutoff.” Does it mean you must score higher than the number, or equal to/higher than? Asking because my daughter scored 222 in Maryland. Haven’t heard from the school as of yet.
Equal to or higher. Your school may just be waiting.
Hi Art. While they don’t publish the exact GPA cut-off, would you consider 3.8X (unweighted) with no C’s a safe qualifying GPA?
J S,
I just don’t have the data. My recommendation would be to stay positive, assume that it’s sufficient, complete your Finalist app, and then get on with the important job of getting admitted to college!
Hi, is 214 in AZ absolutely confirmed? Thanks!
The cutoffs are correct.
If you had to send an alternate entry of a SAT score due to illness on the day of the PSAT, does that SAT score act also as the confirming SAT score or do you have to retake another SAT? Thank you.
I would check with NMSC on that. I think it came up last year, but I don’t remember where things fell. I want to say that it could serve as the confirming score.
What should we do at this point if our school says they haven’t received anything (not that they can’t won’t say, but that they say they actually haven’t gotten anything) but we met the criteria according to what you posted? Our kid has a 211 in Arkansas. I think our school has never had a National Merit Semi-Finalist (or even commended) before – we had to push them to even offer the PSAT to make this possible.
You can call NMSC and see if they are now able to confirm that you are a Semifinalist. If so, then you (or you and NMSC) will need to work with your school, track down your paperwork, and learn how to submit the Finalist application. You DO the application. But the school has to write the recommendation and SUBMIT the application.
Hi Art,
I know based on the cutoff scores that my son has qualified and, when I asked the principal, she broadly smiled and says she has a letter on her desk, but wants to wait until the pep rally at the end of September to make the announcement. While I think it is sweet that she wants to make a big deal out of it, I am anxious to see the actual confirmation so he can get started on his application. When I searched the National Merit Website, all I could see was a generic press release explaining National Merit. Where can I find a list of names? (Apparently the local media didn’t care about the press release.)
Anonmom,
There are no lists available beyond what NMSC shares with the press (NMSC does not share those lists with the public) and schools. If you are really concerned that your son is not a Semifinalist, you can try calling NMSC. They will usually confirm a name at this point. The essay prompt should be unchanged, so your son can already start preparing his essay. It’s nice to have the letter, but not having it should not pose much of an obstacle.